our websites:
quick contact:
- JBC 2,JLT, PO Box 212889 Dubai, United Arab Emirates
- +971 55 489 4873
- info@rgefertilizer.com
Search
People also search for:
Monoammonium Phosphate (MAP)
Boost your brands creative presence and stand out in the market.
- Home
- Phosphorus Fertilizers
- Monoammonium Phosphate (MAP)
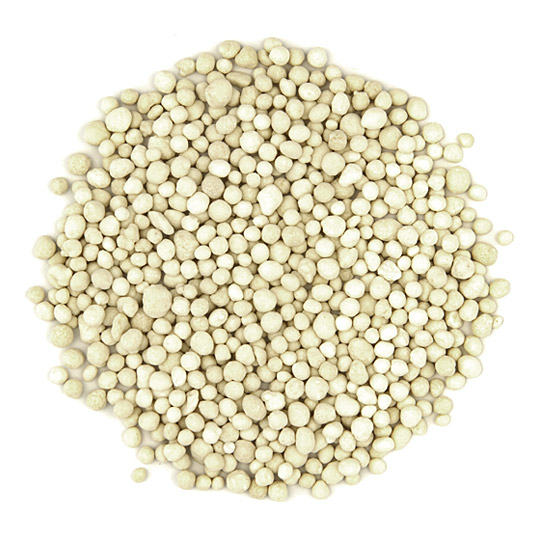

Monoammonium Phosphate (MAP)
Monoammonium Phosphate (MAP), commonly known as MAP, is a chemical fertilizer with the chemical formula NH4H2PO4. This substance is widely used as a phosphatic fertilizer in agriculture and plays a significant role in enhancing plant growth and health. Due to its high phosphorus content, Monoammonium Phosphate is highly beneficial for plants and dissolves quickly in water, making it easily absorbed by plants in moist soils.
Features of Monoammonium Phosphate:
- High Solubility: Due to its high solubility in water, this fertilizer dissolves quickly in the soil and provides the essential nutrients required by plants.
- Best Application Time: The best time to apply MAP is in spring and autumn when plants have higher nutrient requirements for phosphorus and nitrogen.
- Wide Application: Besides agricultural use, MAP is also employed in fire extinguishing agents.
MAP Production Method:
Monoammonium Phosphate is produced by combining ammonia (NH3) and phosphoric acid (H3PO4) in equal proportions. The resulting compound is then processed into granules or powder. MAP produced in this way is used as a granular fertilizer to correct nitrogen and phosphorus deficiencies in various soils.
Role of MAP in Agriculture:
Monoammonium Phosphate serves as a phosphatic fertilizer that helps increase root growth, improves photosynthesis, and enhances plant resistance to diseases and harsh environmental conditions. The phosphorus in MAP supports the plants’ energy transfer, which is crucial for flowering and fruiting. Additionally, the nitrogen in MAP accelerates vegetative growth.
Benefits of Using Monoammonium Phosphate:
- Increased Crop Yield: MAP helps plants to produce better yields and shortens the time to harvest.
- Enhanced Phosphorus and Nitrogen Absorption: The fertilizer aids in the rapid absorption of phosphorus and nitrogen by plant roots.
- Increased Plant Resistance: MAP increases plant resistance to cold and adverse conditions.
Applications in Different Soil Types:
- Alkaline Soils: MAP is more effective in alkaline soils, as ammonium creates an acidic zone around plant roots, which increases the solubility of phosphate compounds and enhances absorption by plants.
- Neutral or High pH Soils: MAP is also suitable for soils with a high pH, helping to improve nutrient uptake.
Uses of Monoammonium Phosphate (MAP)
Monoammonium Phosphate (MAP) is a versatile chemical compound with applications in various industries, primarily agriculture and fire safety.
Agricultural Uses:
- Fertilizer: MAP is a popular fertilizer due to its high solubility in water and its ability to provide both nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) to plants. These nutrients are essential for plant growth and development.
- Starter Fertilizer: MAP is often used as a starter fertilizer for crops like corn, as it provides immediate nutrients to young plants.
- Foliar Fertilizer: MAP can be applied as a foliar fertilizer, directly spraying it onto plant leaves to provide quick nutrient uptake.
Non-Agricultural Uses:
- Fire Extinguishers: MAP is a key component in dry chemical fire extinguishers. When discharged, the fine MAP powder smothers fires by interrupting the chemical chain reaction of combustion.
- Food Additive: In some cases, MAP is used as a food additive, particularly in baking powders, where it acts as a leavening agent.
It’s important to note that while MAP is a valuable resource, its use should be carefully considered and applied according to local regulations and best practices to avoid environmental and health risks.